This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.


ITEMLIST
Products Infomation

High-precision wet classifier equipped with our newly developed rotor
Classifier can arbitrarily adjust the particle size distribution of submicron (several hundred nanometers) to single micron (several micrometers) fine particles present in slurry.
Adjustment is performed by removing fine particles (small particles) or by removing coarse particles (large particles).
Particle diameter to be removed can be freely controlled by the rotational speed of the rotor.
Classifier features removing with higher precision than conventional machines.
SATAKE i Classifier
Maker:
SATAKE MultiMix Corporation
SATAKE i Classifier is equipped with a classifying rotor which rotates at high speed. The classifying rotor has a classification blade to stabilize the centrifugal field.
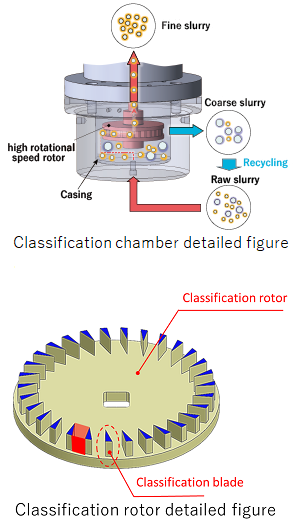
■Flow path
When raw slurry is pumped into the classifier, some fluid passes between the blades of the rotor and goes inside the rotor.
Fine slurry passes through the hollow shaft and is discharged outside the machine. Meanwhile, coarse slurry is discharged from the classifying rotor by centrifugal force and re-supplied as raw slurry.
■Classifying rotor
i Classifier’s classifying rotor is designed with an optimal shape based on many classification tests and CFD flow analysis optimization so that the classification particle diameter is constant in the classification chamber. We succeeded in straightening the flow inside the classification chamber and the rotor, dramatically improving classification accuracy.
■Principle of classification
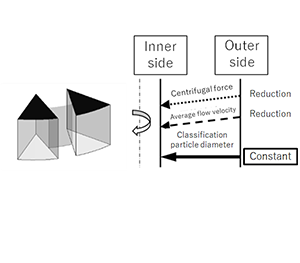 The particles at the outer end of the rotor are acted upon by the centrifugal force generated by the rotational motion of the fluid and the drag (buoyancy) caused by the radial movement of the particles.
The particles at the outer end of the rotor are acted upon by the centrifugal force generated by the rotational motion of the fluid and the drag (buoyancy) caused by the radial movement of the particles.
There is a particle size “= classification particle diameter” where these external forces are exactly balanced.
Particles larger than the classification particle diameter (coarse particles) receive a large centrifugal force and cannot enter the rotor because they move outward. Particles smaller than the classification particle diameter (fine particles) can enter the rotor by riding on the liquid flow, and only these fine particles are recovered outside the machine as slurry.
■Throughput
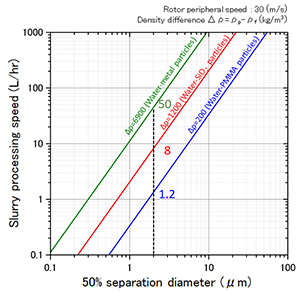
The graph shows the throughput of the machine. (Material: metal, SiO2, PMMA)
The throughput varies depending on the raw material and the desired classification size.
How to read the graph (Example) When the 50% separation diameter is 2 (μm)
The slurry processing speed is:
PMMA particles: 1.2 (L/hr)
SiO2 particles: 8 (L/hr)
Metal particles: 50 (L/hr)
∗ When water is used as a dispersion medium
Please contact us about the throughput for raw materials other than the above.
Classification process example
①Silica fine particles (ρ: 2200 kg/m3) – Fine particle and coarse particle remove process using aqueous dispersion
[Aims]
1.5 μm or less removal and
4.5 μm or more removal
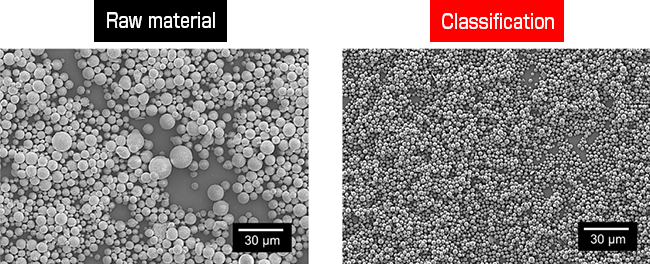
(1) Silica fine particles (density: 2200 kg/m3) – Aqueous dispersion Fine particle remove process
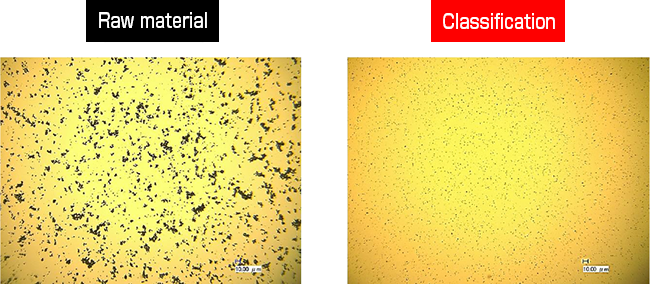
Fine particles adhering to the surface of the raw material are completely removed by the fine particle remove process.
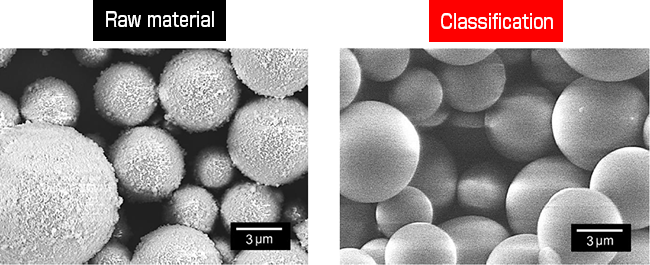
(2) Silica fine particles (density: 2200 kg/m3) – Aqueous dispersion Coarse particle remove process
The coarse particle remove process after the fine particle remove process gives particles with high monodispersity.
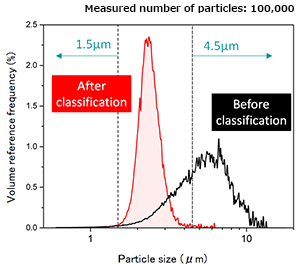
Silica fine particles (ρ: 2200 kg/m3) – Aqueous dispersion Particle size distribution
② Acrylic fine particles (1200 kg/m3) – Aqueous dispersion Coarse particle remove process
The particle size distribution can be freely controlled by the rotor peripheral speed.
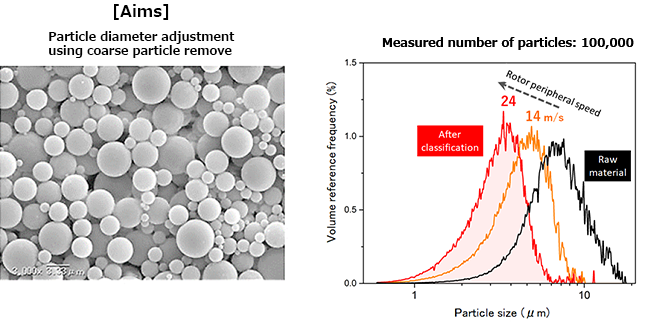
③ Barium titanate (6000 kg/m3) – Aqueous dispersion Coarse particle remove process
The coarse particle cut removes the coarse particles and the distribution has a mode diameter of about 0.6 μm.
SATAKE i Classifier Machine Specifications
| Item | Specifications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product name | SATAKE i Classifier | ||||
| Main unit dimensions | 600×900×1600 mm | ||||
| Weight | Approx. 200 kg | ||||
| Rotational speed | 2000–7000 min-1 | ||||
| Peripheral speed | 10–30 m/s | ||||
| Throughput | 20 L/hr (maximum) | ||||
| Classification chamber capacity | 0.4 L | ||||
| Wetted part material | Rotor | SUS304,316L/zirconia (planned) | |||
| Vessel | SUS304,316L/zirconia (planned) | ||||
| O-ring | FFKM | ||||
| Others | SUS304,316L | ||||
| Shaft seal part | Double mechanical seal | ||||
| Seal liquid | Water/organic solvent | ||||
| ■SATAKE i Classifier Utility Specifications | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Specifications | ||
| Power supply | AC 200V, 3-phase, 50/60Hz | ||
| Power | 2200 W (main unit only) | ||
| Compressed air or nitrogen | 0.8 MPa (for sealing liquid pressurization) | ||
| Cooling water | 0.1–0.2 MPa 2–3 L/min | ||
∗We are continually developing our products to improve classification and performance.
We will notify you when there are specification changes, etc.






